2.1 Wave propagation in rectangular waveguide
The wave is an electromagnetic wave if the Maxwell equations are obeyed. This allows defining a set of wave equations, which for an electric field is described with the following formula:
![]()
Solving this equation under the boundary conditions as in a waveguide results in the following relation:
![]()
It defines the phase constant (in a lossless case it is equal to the propagation constant g) as a sum of squares of propagation constant in the direction of propagation bz and a ![]() constant. The
constant. The ![]() constant is strictly related to the waveguide dimensions and the waveguide mode that is propagating:
constant is strictly related to the waveguide dimensions and the waveguide mode that is propagating:
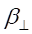
where m and n stand for waveguide mode indexes (corresponding to a number of wave halves existing along a and b waveguide sides respectively), a and b are the width and height of a waveguide.
It needs to be noted that for a given waveguide dimensions and waveguide mode (m,n indexes), propagation along the waveguide will be possible only in a specific frequency range. The lower frequency of that range is called cut-off frequency and can be determined in the following way:
![]()
![]()

It is clearly seen that the cut-off frequency strictly depends on parameters of a medium filling the waveguide (μ,ε), waveguide dimensions (a,b) and waveguide mode indexes (m,n).